- Inspiring People -
- 7mins -
- 190 views
Britain trials potentially game-changing blood test that detects cancer before symptoms appear
The Galleri test, to be trialled on thousands of Britons by the National Health Service this month, can detect cancers that are not routinely screened for and can pinpoint where in the body the disease is coming from with a high degree of accuracy.
Britain’s NHS launches world first trial for new cancer test
Last Monday, 13 September 2021, Britain’s NHS (National Health Service) launch the world’s largest trial of a revolutionary new blood test that can detect more than 50 types of cancer before symptoms appear. The first people to take part will have blood samples taken at mobile testing clinics in retail parks and other convenient community locations. The Galleri™️ test checks for the earliest signs of cancer in the blood and the NHS-Galleri trial, the first of its kind, aims to recruit 140,000 volunteers in eight areas of England to see how well the test works in the NHS.

What is the Galleri cancer test and who is it for?
The Galleri cancer test is a simple blood test that looks for the earliest signs of cancer, particularly those that are typically difficult to identify early or for which there are no NHS screening programmes – such as lung, pancreas or stomach cancers.
Developed by Californian firm Grail, the test can detect subtle changes caused by cancers, when patients may have no other obvious symptoms. It works by finding chemical changes in fragments of genetic code – cell-free DNA (cfDNA) – that leak from tumours into the bloodstream. The signal does not mean that a person definitely has cancer. It just means that they might have cancer, and that they will need to have some follow-up tests to check.
"This quick and simple blood test could mark the beginning of a revolution in cancer detection and treatment here and around the world," says NHS England’s Chief Executive Amanda Pritchard.
Source: BBC
How the trial will work
Participants will be asked to give a blood sample at a locally based mobile clinic. They will then be invited back twice – after 12 months and two years – to give further samples. Half those taking part will have their blood screened with the Galleri test immediately. However, others will simply have their samples stored away to be tested in the future – should they go on to be diagnosed with cancer.
This is because the trial is what’s known as a Randomised Control Trial (RCT). It will allow scientists to see whether cancer is detected significantly earlier among people who have their blood tested straight away.
People will only know they’re in the first test group if they are among the small minority whose blood test detects potential signs of cancer. Those people will be contacted by the trial nurses by phone and referred to an NHS hospital for further tests.
Everyone taking part will be advised to continue with their standard NHS screening appointments and to still contact their GP if they notice any new or unusual symptoms.
Source: BBC

Initial results of the study are expected by 2023
The test is a simple blood test that research has shown is particularly effective at finding cancers that are typically difficult to identify early – such as head and neck, bowel, lung, pancreatic, and throat cancers.
It works by finding chemical changes in fragments of genetic code-cell-free DNA (cfDNA) that leak from tumours into the bloodstream. The NHS is already sending out letters inviting tens of thousands of people from different backgrounds and ethnicities aged between 50 and 77 to take part.
Participants, who must not have had a cancer diagnosis in the last three years, will be asked to give a blood sample at a locally based mobile clinic and they will then be invited back after 12 months, and again at two years, to give further samples. The trial is part of the NHS’s efforts to increase the proportion of cancers detected early by the end of the Long Term Plan.
The NHS-Galleri trial is being run by The Cancer Research UK and King’s College London Cancer Prevention Trials Unit in partnership with the NHS and healthcare company, GRAIL, which has developed the Galleri test.
It is operating with the support of eight NHS Cancer Alliances across England that span Cheshire and Merseyside, Cumbria, Greater Manchester, the North East, West Midlands, East Midlands, East of England, Kent and Medway, and South East London. For the purposes of the trial, only people living in these areas will be invited.
Initial results of the study are expected by 2023 and, if successful, the NHS in England plans to extend the rollout to a further one million people in 2024 and 2025.
Patients whose cancer is found early – known as stage one or two – typically have a broader range of treatment options available to them, which can be curative and are often less aggressive.
A patient whose cancer is diagnosed at the earliest stage typically has between five and 10 times the chance of surviving compared with those found at ‘stage four.’
Source: NHS
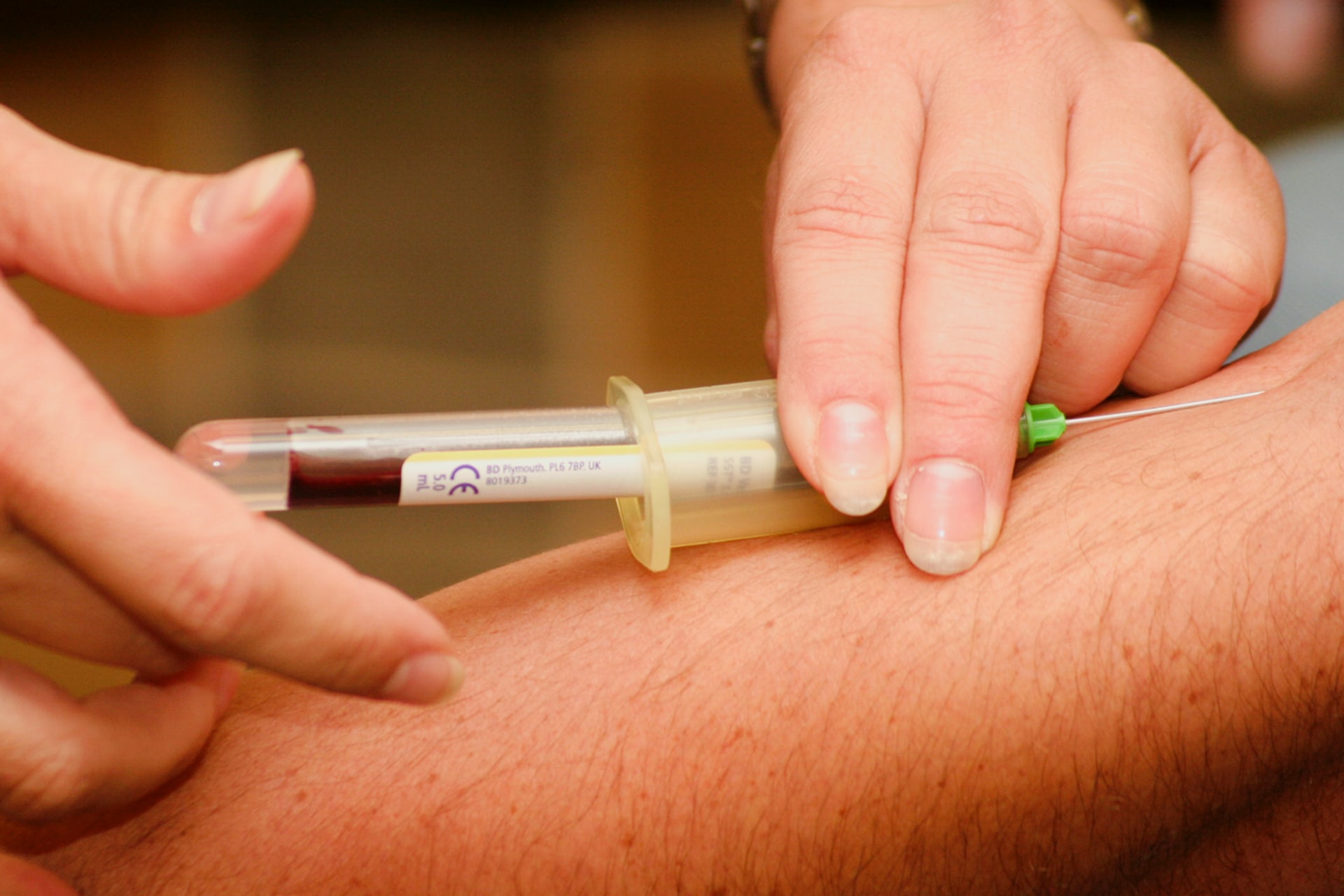
NHS chief executive Amanda Pritchard said:
“This quick and simple blood test could mark the beginning of a revolution in cancer detection and treatment here and around the world. By finding cancer before signs and symptoms even appear, we have the best chance of treating it and we can give people the best possible chance of survival.
“The NHS has a successful track record of leading the way on innovations in cancer diagnosis and treatment, from CAR-T therapy to COVID-friendly drugs. The Galleri blood test, if successful, could play a major part in achieving our NHS Long Term Plan ambition to catch three quarters of cancers at an early stage, when they are easier to treat.
“So if you are invited, please take part – you could be helping us to revolutionise cancer care and protect yourself.”
Source: NHS

The test could be a game-changer for early cancer detection
Health and Social Care Secretary Sajid Javid said:
“The UK’s world leading scientists continue to pioneer innovative cancer diagnosis and treatments so our brilliant NHS staff have the tools to spot the disease as early as possible and give people the care they need. Early diagnosis can save lives and this revolutionary new test can detect cancers before symptoms even appear, giving people the best possible chance of beating the disease. Ensuring fewer people need treatment for advanced cancer is vital for patient care and another example of the NHS innovating to be more efficient – which will be crucial in bringing down the backlog.”
Prof Peter Sasieni, Director of The Cancer Research UK & King’s College London Cancer Prevention Trials Unit and one of the trial’s lead investigators, said: “We need to study the Galleri test carefully to find out whether it can significantly reduce the number of cancers diagnosed at a late stage. The test could be a game-changer for early cancer detection and we are excited to be leading this important research. Cancer screening can find cancers earlier when they are more likely to be treated successfully, but not all types of screening work.”
Source: NHS

The test is strong at detecting deadly cancers and has a very low rate of false positives
Sir Harpal Kumar, President of GRAIL Europe, said:
“We’re delighted to partner with the NHS to support the NHS Long Term Plan for earlier cancer diagnosis, and we are eager to bring our technology to people in the UK as quickly as we can. The Galleri test can not only detect a wide range of cancer types but can also predict where the cancer is in the body with a high degree of accuracy. The test is particularly strong at detecting deadly cancers and has a very low rate of false positives.”
Stuart Devereux, a serving fire brigade officer, will be among the first participants in the NHS-Galleri trial in Runcorn. He said: “Being able to contribute to this study that could save many lives was a very easy decision to make, and it’s not going to take up much of my time. Working in the fire service, we save lives by preventing rather than fighting fires and in a similar way I’m keen to be involved in helping the NHS to trial new technology that can detect cancer before symptoms appear. We will only make progress in tackling cancer if people come forward for trials like this.”
Source: NHS


