
- Sustainable Planet -
- 6mins -
- 440 views
Did you know the Earth is actually rich with untapped clean energy resources?
Between solar, algae, tidal power, and geothermal energy, we have enough to meet our needs many times over.
Sun, Seaweed and Subterranean heat among the long-term clean and sustainable energy solutions
At present our energy supply is mainly based upon fossil fuel energy sources. Due to decreasing resources, paired with a worldwide increase in energy demand, and the resultant growth of environmental pollution, it has become crucial to tap into other sources to ensure a clean and sustainable energy supply in the long term. Solar, macro-algal (seaweed forests), tidal, and geothermal energy are all exciting areas of research, all with promising results and staggering statistics. Here’s what we found out, with thanks to Hashem Al-Ghaili.
1. Macro-algal residue from seaweed forests for biomethane production
According to a report published in 2016 by The National Center for Biotechnology Information, the increased use of terrestrial crops for biofuel production and the associated environmental, social and ethical issues has led to a search for alternative biomass materials. While terrestrial crops offer excellent biogas recovery, they compete directly with food production, requiring farmland, fresh water and fertilisers.
The use of marine macro-algae (seaweed forests) for the production of biogas circumvents these problems. Their potential lies in their chemical composition, their global abundance and knowledge of their growth requirements and occurrence patterns.
Any such biomass industry should focus primarily on the use of residual and waste biomass to avoid competition with the biomass requirements of the seaweed food industry, which has occurred in the case of terrestrial biomass.
Overabundant seaweeds represent un-utilised biomass in shallow water, beach and coastal areas. The excessive richness of nutrients this causes damages marine ecosystems and impairs local tourism; this excessive biomass could serve as biogas feedstock material.
The residues from biomass processing in the seaweed industry are also of interest. This is a rapidly growing industry with algae now used in the comestible, pharmaceutical and cosmetic sectors. The simultaneous production of combustible bio-methane and disposal of undesirable biomass in a synergistic waste management system is a concept with environmental and resource-conserving advantages.
Read the full in-depth report by The National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

2. The magic of the moon: harnessing the tidal ebb and flow
Through the millennia our ancestors knew when to plant simply by looking at it, and ships’ captains circumnavigated the globe by it…. now could its ebb and flow could power our industries and cities?
After solar power, lunar power — or more precisely tidal power — is extremely well positioned to provide us with a sustainable and limitless power source for years to come, or "many moons," you might say.
It’s scalable and it’s limitless, as long as the tides keep ebbing and flowing!

3. Geothermal heat: the heat energy that is stored beneath the surface of the earth
Regardless of the whatever the weather is doing outside, it’s always hot deep beneath our feet. Around 99 per cent of the material that makes up the Earth’s mass has a temperature of above 1,000 degrees Celsius. That can be used as an inexhaustible source of heat — and one that presents huge opportunities for the energy transition.
Around 6,350 kilometres beneath our feet, liquid iron oozes at temperatures of up to 7,000 degrees Celsius. The temperature decreases the closer you move towards the surface. In the final top 10 km of the Earth’s crust, the temperature is an average of just 15 degrees Celsius.
However, it has been calculated that the heat contained within the earth’s outermost layer is sufficient enough to cover the current energy needs of all the entire global population — and it could do this more than 100,000 times over, electricity generation included.
Almost unbelievably, beneath the surface of the Federal Republic of Germany alone, there is enough heat at between 3—7 km depth to supply Germany with the energy it needs for 10,000 years – 24 hours a day, irrespective of the weather, and causing zero harm to the climate. The term to describe this source is ‘geothermal’ heat. This is the heat energy that is stored underneath the surface of the earth.
Source: BMWi-energiewende.de

4. Solar electricity from North Africa can be transmitted via HVDC to Europe
At present our energy supply is mainly based upon fossil fuel energy sources. Due to decreasing resources, paired with a worldwide increase in energy demand, and the resultant growth of environmental pollution, it has become crucial to tap into other sources to ensure a clean and sustainable energy supply in the long term.
With this in mind, let’s consider the large potential of solar energy in North Africa which, in theory, meets the world’s energy demand many times over. On-site solar electricity can be produced by solar thermal power plants and then be transmitted via high voltage direct current transmission (HVDC) over long distances to Europe.
From the thesis ‘Eco-balance of a Solar ElectricityTransmission from North Africa to Europe’, by Nadine May
Source: Technical University of Braunschweig, Faculty for Physics and Geological Sciences

Renewables and energy efficiency are the future, and the climate and environment will thank us
Alternatives must be found which can guarantee a secure energy supply, while preserving the climate and the environment. Furthermore, this energy must be provided free of risks and with low costs in order to avoid military conflicts over energy resources and additional environmental pollution. Renewable energies meet all these requirements of a sustainable energy supply today and in the future.
There are good reasons why home-owners should switch to systems based on renewables and focus on raising energy efficiency. Not only will they save money, but their living comfort will also improve – as will the value of their property. The climate will thank them for their efforts, as well.
Change the norm
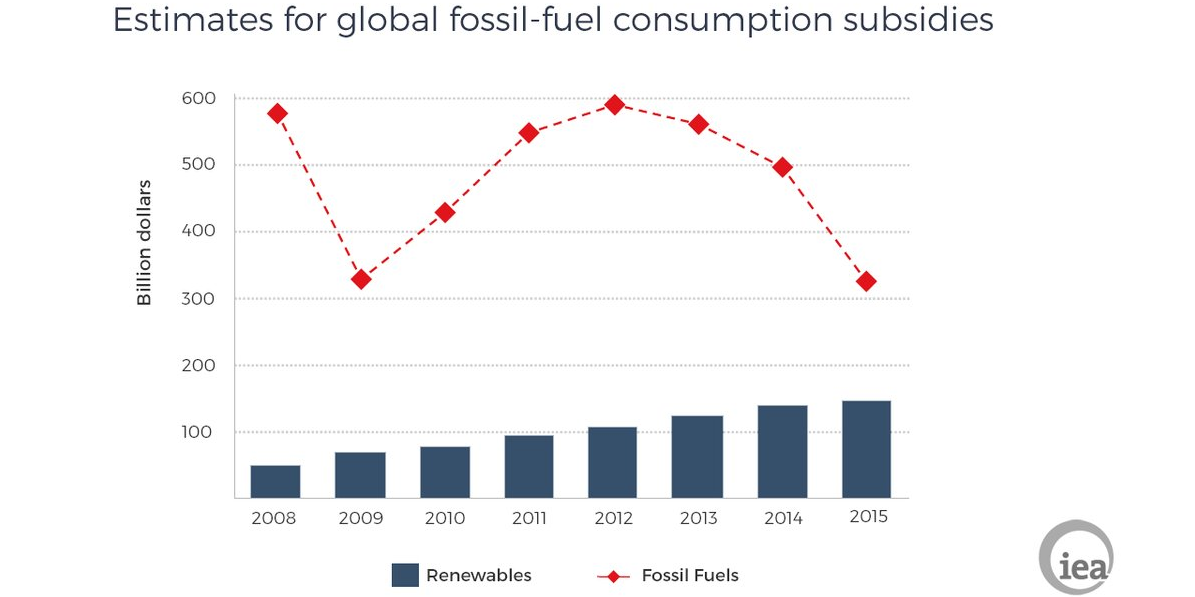
There are people who say that renewable energy costs too much money. That you have to spend a lot of money subsidizing these forms of energy in order to make them possible.
But did you know that fossil fuels get over twice as much subsidies as renewable energy? And twice as much is almost nothing in comparison to what they used to get in subsidies.
Fossil fuels received a staggering 325 billion dollars a year on subsidies in 2015, whereas renewable energy only got 150 billion.
Luckily, the subisdies for fossil fuels are declining and subsidies for renewable energy are on the rise. By choosing renewable energy over fossil fuels, we can somewhat help speed up this process and move towards a world where renewable energy is the norm.

